BFS (너비 우선 탐색, Breadth-First Search)
그래프 탐색.
하나의 정점으로부터 시작하여 차례대로 모든 정점들을 한 번씩 방문하는 것
너비 우선 탐색.
루트 노드(혹은 다른 임의의 노드)에서 시작해서 인접한 노드를 먼저 탐색하는 방법
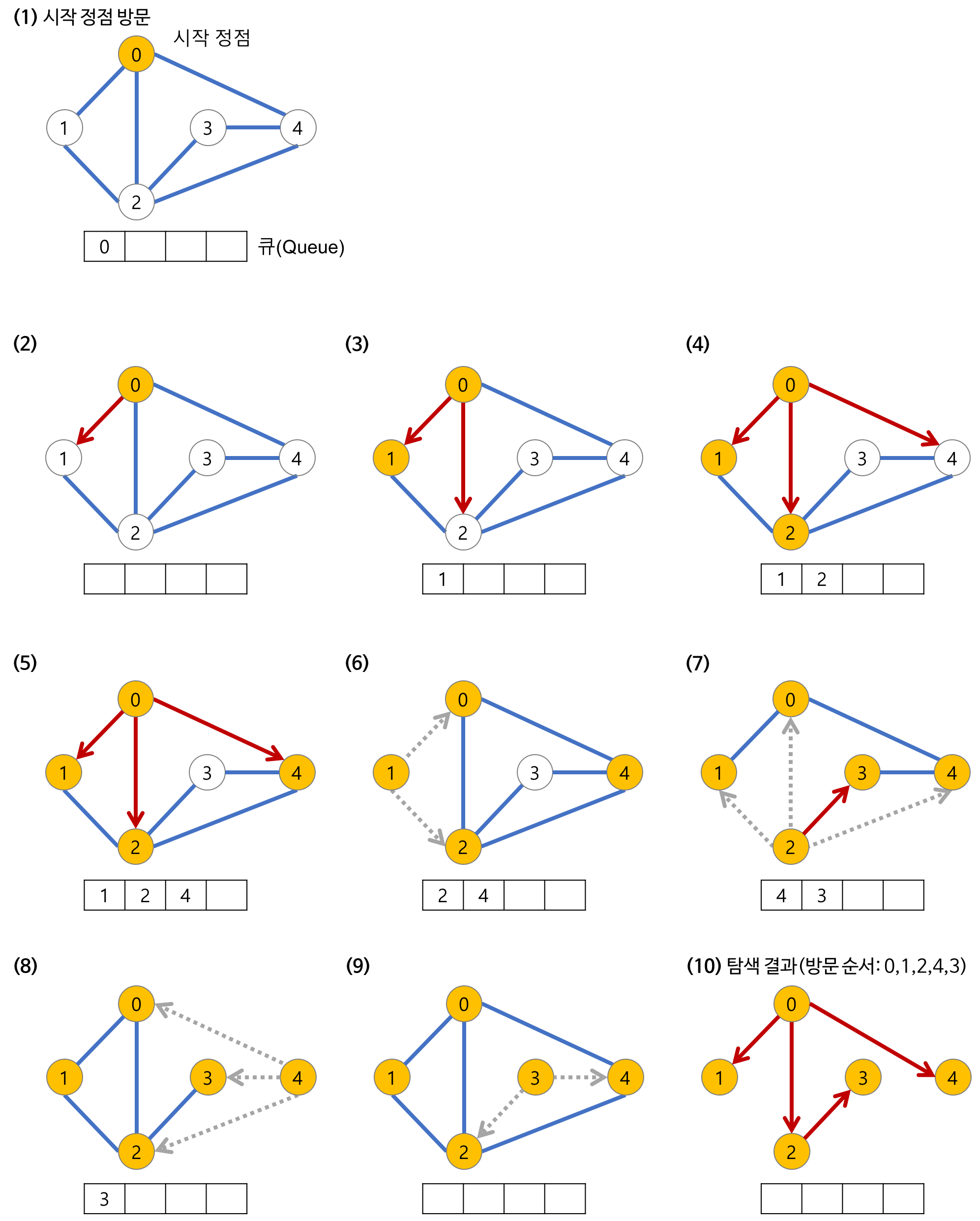
시작 정점으로부터 가까운 정점을 먼저 방문하고 멀리 떨어져 있는 정점을 나중에 방문하는 순회 방법이다.
깊게(deep) 탐색하기 전에 넓게(wide) 탐색하는 것이다.
사용하는 경우: 두 노드 사이의 최단 경로 혹은 임의의 경로를 찾고 싶을 때 이 방법을 선택한다.
BFS(너비 우선 탐색)이 DFS(깊이 우선 탐색)보다 좀 더 복잡하다.
너비 우선 탐색(BFS)의 특징.
직관적이지 않은 면이 있다.
BFS는 시작 노드에서 시작해서 거리에 따라 단계별로 탐색한다고 볼 수 있다.
BFS는 재귀적으로 동작하지 않는다.
차이점은, 그래프 탐색의 경우 어떤 노드를 방문했었는지 여부를 반드시 검사 해야 한다는 것이다.
이를 검사하지 않을 경우 무한루프에 빠질 위험이 있다.
BFS는 방문한 노드들을 차례로 저장한 후 꺼낼 수 있는 자료 구조인 큐(Queue)를 사용한다.
선입선출(FIFO) 원칙으로 탄색
‘Prim’, ‘Dijkstra’ 알고리즘과 유사하다.
https://gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/08/15/algorithm-bfs.html
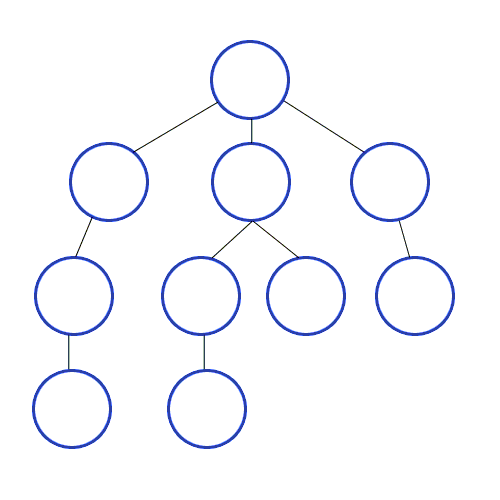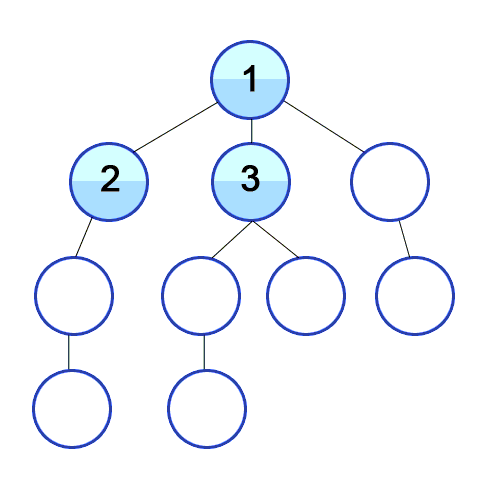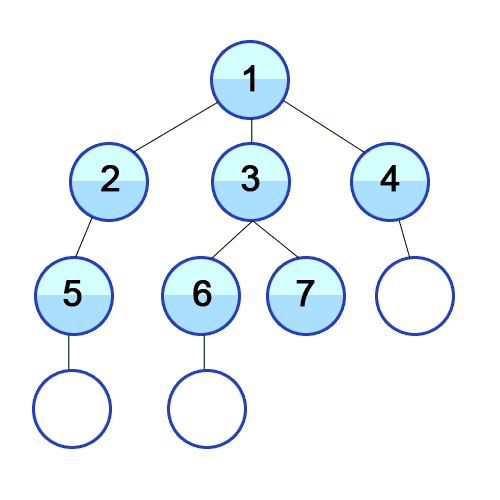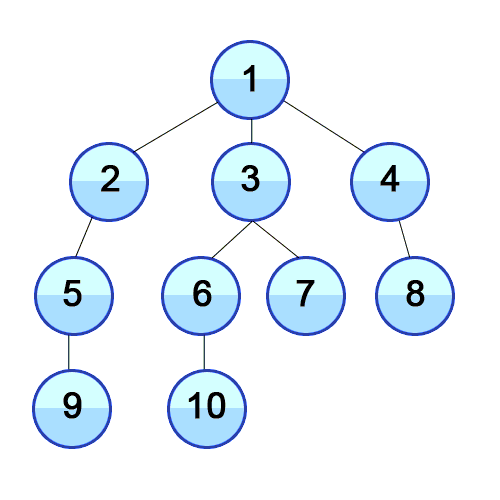
너비 우선 탐색(BFS)의 과정
깊이가 1인 모든 노드를 방문하고 나서 그 다음에는 깊이가 2인 모든 노드를,
그 다음에는 깊이가 3인 모든 노드를 방문하는 식으로 계속 방문하다가 더 이상 방문할 곳이 없으면 탐색을 마친다.
BFS 알고리즘 파이썬 코드
코드 1
def bfs(graph, start):
visited = []
queue = [start]
while queue:
n = queue.pop(0)
if n not in visited:
visited.append(n)
queue += graph[n] - set(visited)
print(visited)
return visited
graph = {'A' : set(['B', 'C']),
'B' : set(['A', 'D', 'E']),
'C' : set(['A', 'F']),
'D' : set(['B']),
'E' : set(['B', 'F']),
'F' : set(['C', 'E'])
}
start = 'A'
print(bfs(graph, start))코드 1 결과.

코드 2
def bfs_paths(graph, start, goal):
queue = [(start, [start])]
result = []
while queue:
n, path = queue.pop(0)
if n == goal:
result.append(path)
else:
for m in graph[n] - set(path):
queue.append((m, path + [m]))
return result코드 3
def bfs(graph, start):
visited = []
queue = [start]
while queue:
n = queue.pop(0)
if n not in visited:
visited.append(n)
queue += graph[n] - set(visited)
print(visited)
return visited
graph = {'A' : set(['B', 'C']),
'B' : set(['A', 'D', 'E']),
'C' : set(['A', 'F']),
'D' : set(['B']),
'E' : set(['B', 'F']),
'F' : set(['C', 'E'])
}
start = 'A'
print(bfs(graph, start))
def bfs_paths(graph, start, goal):
queue = [(start, [start])]
result = []
while queue:
n, path = queue.pop(0)
if n == goal:
result.append(path)
else:
for m in graph[n] - set(path):
queue.append((m, path + [m]))
return result
start = 'D'
goal = 'F'
print(bfs_paths(graph, start, goal))코드 3 결과.

BFS (너비 우선 탐색)의 시간 복잡도
인접 리스트로 표현된 그래프: O(N+E)
인접 행렬로 표현된 그래프:
References
- http://eddmann.com/posts/depth-first-search-and-breadth-first-search-in-python/
- McDowell, G. L. (2016). Cracking the Coding Interview: 189 Programming Questions and Solutions. CareerCup, LLC.
- http://blog.eairship.kr/269
- https://gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/08/15/algorithm-bfs.html
- http://ejklike.github.io/2018/01/05/bfs-and-dfs.html
'알고리즘 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 20. 큐와 스택 (FIFO, LIFO) (0) | 2019.10.07 |
|---|---|
| 19. DFS (깊이 우선 탐색) (0) | 2019.10.07 |
| 17. 프림 알고리즘 (0) | 2019.10.05 |
| 16. 크루스칼 알고리즘 (0) | 2019.10.04 |
| 15. 그리디 알고리즘 (동전, 거스름돈 문제) (0) | 2019.10.03 |



